FORCE
- What causes/makes a body at rest to move?
- What causes the same body in motion to stop?
- Force can cause a change in the way the object moves
- Change its size or shape
- Change the direction in which an object is moving
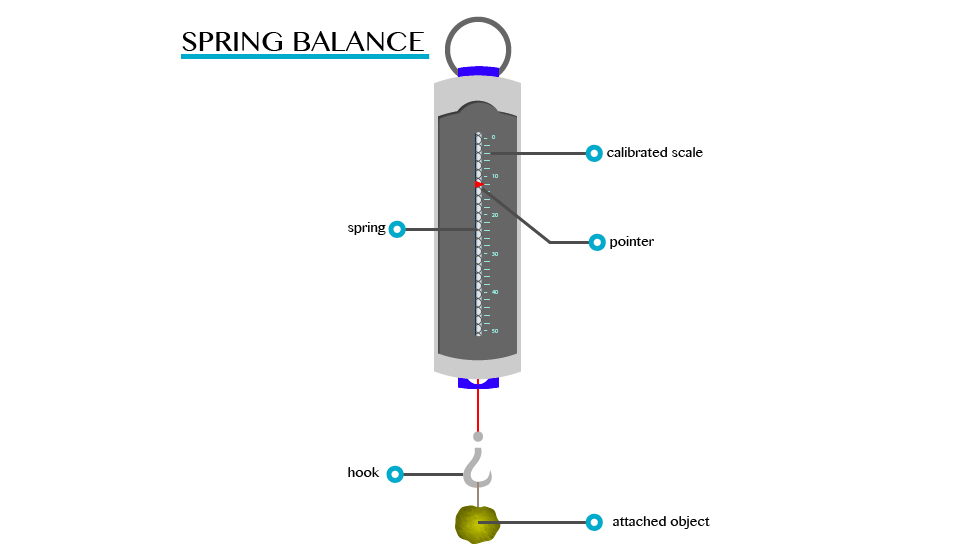
A spring balance can be used to measure small forces. It consists of a coiled spring fixed to the other end with a hook at the other end. The body upon which the force acts is attached to the hook. The distance through which the spring is stretched is directly proportional to the force applied by the balance.
- Fundamental forces
- Non fundamental forces
- The force of gravity
- The electromagnetic force
- The strong nuclear force
- The weak nucleus force
The force of gravity is the pull by which the earth, moon and other very large bodies attract other objects towards themselves. It is commonly referred to as the weight of the object that is attracted.
In mechanics, a freely falling body in the air moves down irrespective of its mass. This is due to force of gravity.
Example 1
Where acceleration due to gravity on the earth, g = 9.8m/s2
It pulls (attracts) objects towards the centre of the earth.
It is directly proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the greater the mass the greater the pull of gravity.
It is strong when the mass is closer to the centre of the earth.
It is the gravitation’s field strength (10N/Kg)
It is the acceleration of free fall (10m/s2
It is basically an attractive force
It is a non-central force (does not act at the centre)
It is stronger than gravitational force
It is a short-range force that is it operates only up to distance of the order of 10-14m
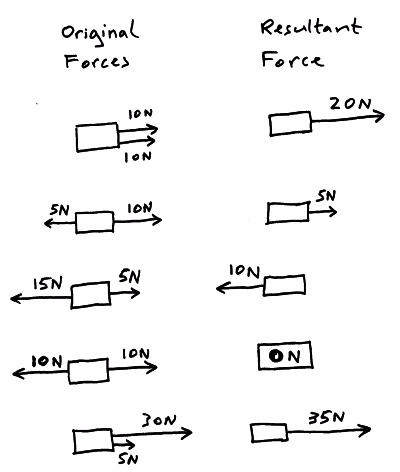
The object will accelerate or decelerate (speed up or slow down).
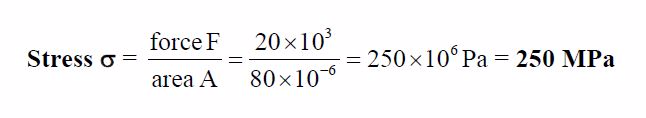




















Leave a Reply