Concept of Pressure
Pressure is defined as the force per unit area. OR Pressure is the force acting normally (perpendicularly) per unit surface area.
Where
- P – Pressure
- F – Force
- A – Area
The S.I Unit of Pressure
The SI unit of Pressure is Newton per square metre (N/M2). This unit is usually referred to as the Pascal (Pa).
The other units of pressure are atmosphere, torr bar and mmHg.
1 atmosphere = 780mmHg
1 atmosphere = 1 105 N/M2 = 1bar (used by meteorologists)
When a man lifts a bucket of water by its handle that is made with a thin metal, he would experience some discomfort but if the bucket was made with a thicker handle the discomfort will be much less if any.
This is because the area over which the force is applied is larger.
The pressure in solid depends on the surface area of contact. A force (F) applied onto a small area exerts a higher pressure as compared to when it is applied onto a large surface.
Example 1
A block of wood that weighs 30N and measures 5m by 10m by 4m. If it was placed on a table with the largest possible area (5mx10m) in contact with table, exerts less pressure than it would when placed with its smallest possible area (5mx4m) in contact with table.
Data:
Pressure = 1.5 N/M2
A tip of needle has a cross- sectional area of 1×106m2. If doctor applies a force of 2N to a syringe that is connected to the needle, what is pressure is exerted at the tip of the needle?
The pressure extended by the needle lip is 2.0×107N/m2
A rectangle metal block with sides 105m by 1.0m by 1.2m rests on a horizontal surface. If the density of the metal is 7000kg/m3. Calculate the maximum and minimum pressure that the block can exerts on the surface.
(Take the weight of 1kg mass to be 10N)
Solution:
Maximum pressure = 1.05×106N/m2/maximum pressure= 0.7×105N/m2
The Applications of Pressure due to Solids
It is used to make different objects like screw, nails, pins, spears and arrows. This item is given sharp points to increase their penetrating power.
Buildings are constructed with wide foundations to ensure that the weight of the building acts over the layer area.
PHYSICS FROM ONE TOPIC 7: PRESSURE
Pressure in Liquids
A liquid will exert pressure on an immersed object as well as on the walls of the container holding it. Note that the pressure exerted by liquids is due to the weight of the liquid. Also increase in water level in liquid cause increase in pressure.
Hence pressure in liquids is given as hsg.
H= Height of the liquid column
Depth
Density of liquid
Pressure in liquids is characterized using the following parameters
Pressure in a liquid increase with depth
Pressure in a liquid acts equally in all directors
Pressure in a liquid increases with increase in density of the liquid.

As pressure at point A is low due to small height of water above it but at point B the height increase and the distance of water increase while at point C the height is greatest therefore the level of water distance will be large distance.
Demonstration of pressure in a communicating vessel
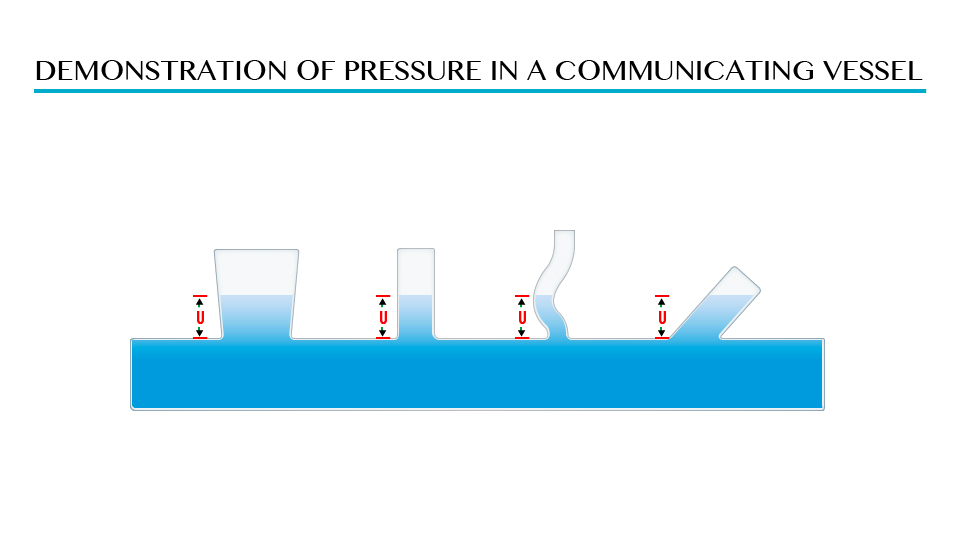
The shape of vessel found in point A, B, C and D is different but the pressure is the same due to the equal height (L) of the liquid above the points.
Example 4
A cube of side 2cm is completely submerged in water so that the bottom of the cube is at a depth of 10cm. use g=10m/s2 and s=1000kg/m3
What is different between the pressure on the bottom of the cable and the pressure on its tap?
Determine the difference in the force on the top and bottom.
What is the weight of the water displaced by the cube?
Data.
mass of displaced water/100=8g = 0.08N
Calculate the pressure at the bottom of tank of water 15m deep due to the water above it is (s=1000kg/m3).
= 1000x10x15=150000N/M2
The Principle of a Hydraulic Pressure
Explain the principle of a hydraulic pressure
Illustration of Pascal’s Principle.
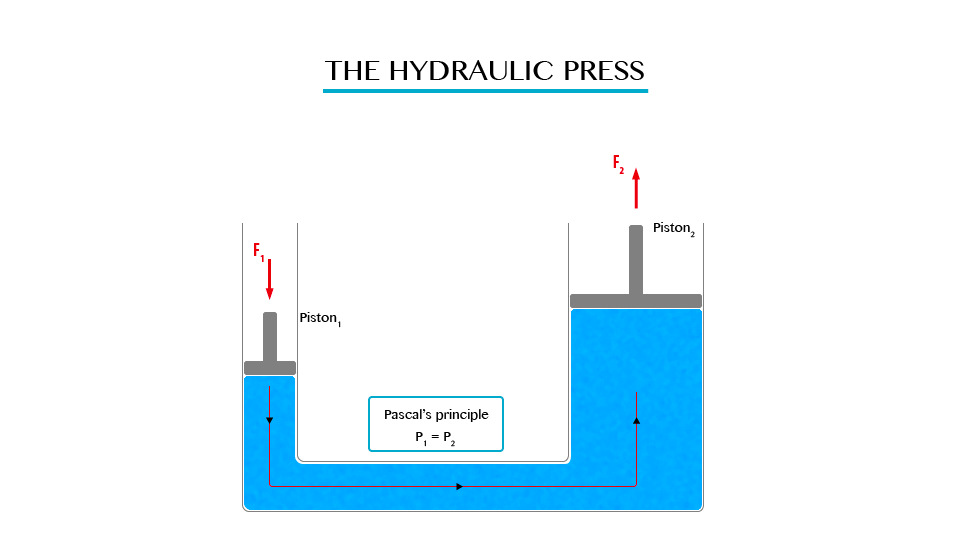
Note: in all side of vessel will experience equal pressure.
From Pascal’s Principle
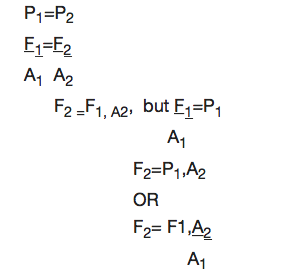
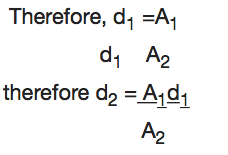
Example 6
A2 = 3X104m2
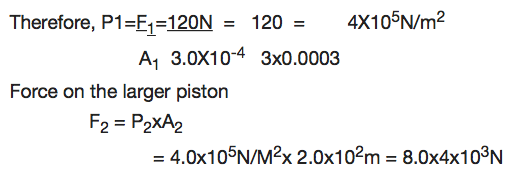
Application of Hydraulic Press
Measure pressure of a liquid
Hydraulic press is used in industries to express bulk items.
Hydraulic brake system
When pressure is applied to the brake pedal, it pushes the piston in the master cylinder forward creating a pressure in the brake fluid. This pressure is transferred to the slave cylinders where it is multiplied and pushes the brake shoes against the brake dram that is attached to the wheel of the vehicle.

It is used in industries in the forming of metals.
Measuring the pressure of liquids using a manometer. Manometer is the device for measuring pressure (commonly gas).
Atmospheric Pressure
The Existence of Atmospheric Pressure
Note. The atmospheric pressure on the earth’s surface and objects on the earth is a approximately 1.01×105N/m2.
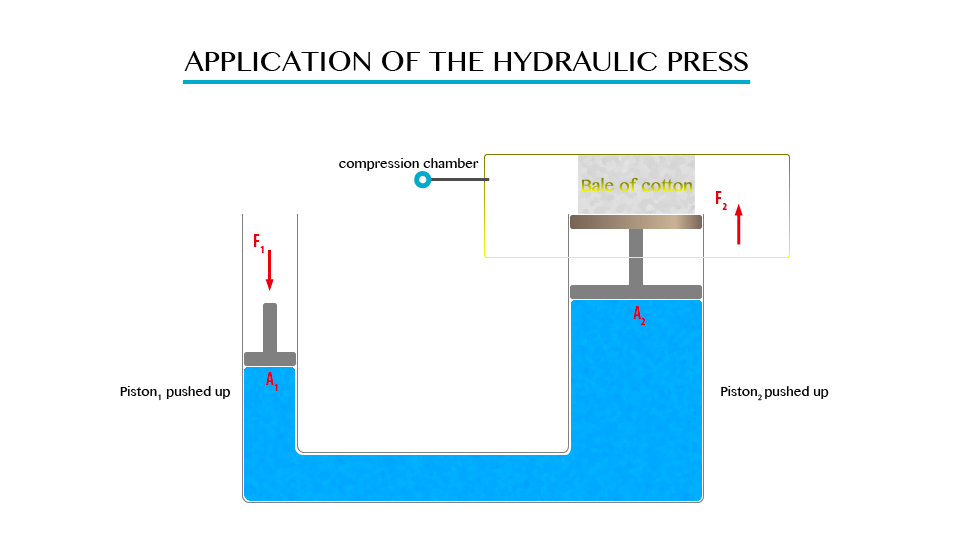
When you fill a glass timber with cord and gentle turned upside down. It will be seen that water will not poured down.
Plunger

Pulling the plunger is not easy. This is so because all the air is squeezed out from the table when the surrounding pressure being high the plunger sticks.
Crushed bottle

When putting hot water in, the bottle is cooled under cold water the steam condenses; leaving partial vacuum inside the bottle consequently the greater atmospheric pressure outside the bottle crushes it in wards.
Identify the applications of atmospheric pressure
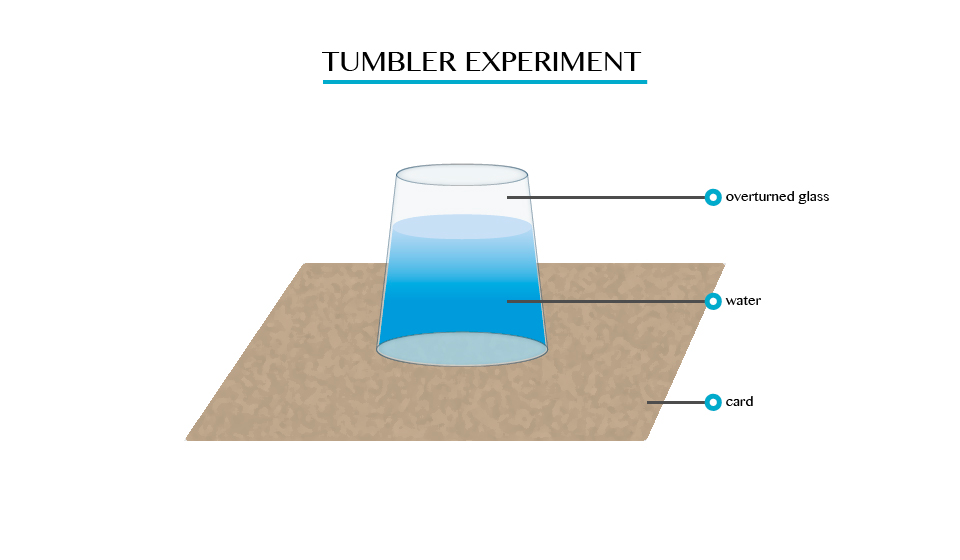
A siphon
siphon is applied in areas and devices that we use everydayIt is used in the toilet flushing cisterns (chain and ball tank). The flush is triggered by a handle that operates a simple diaphragm like piston pump that lifts enough water.
It is used in special rain gauges called siphon rain gauge which are able to automatically drain out excess water.
A siphon cup is a reservoir attached to a gum.
It is used is some drainage systems to drain water to one point.
The lift pump
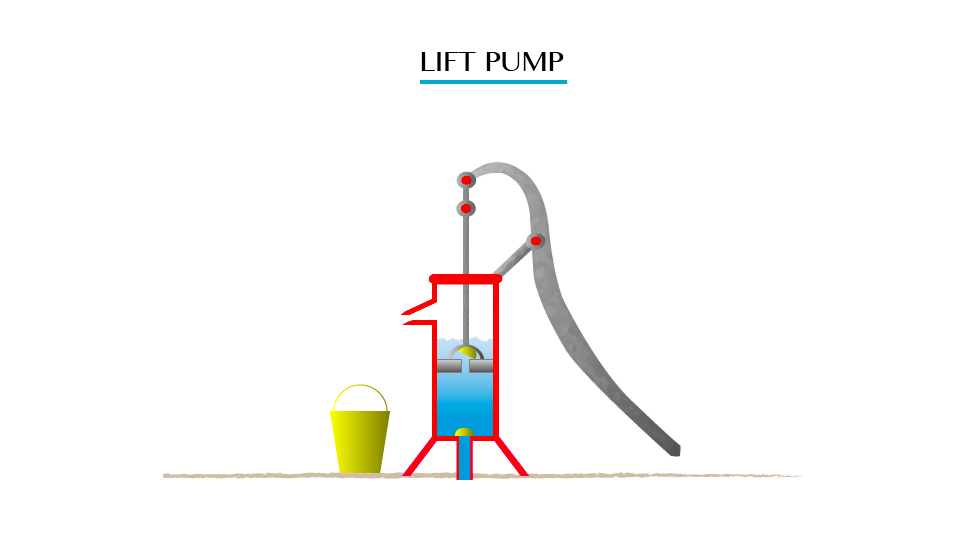
A lift pump is used to raise water from underground sources. This is a pump that is used to lift the liquid, rather than force liquid up.
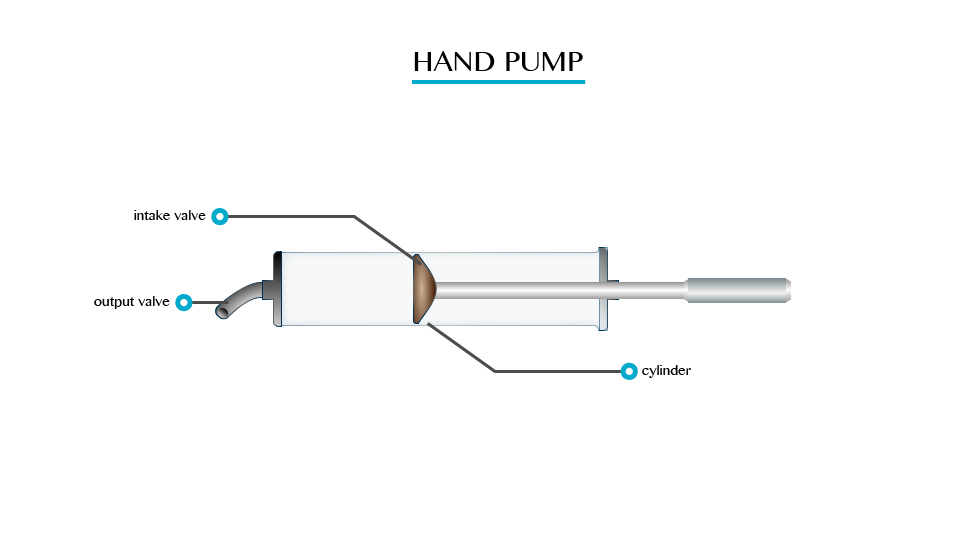
A syringe is a simple piston pump that lifts a tube. The plunger that lifts can be pulled and pushed through inside a cylindrical tube or barrel. This enables the syringe to take in or expel fluid through the opening (nozzle) at the end of the tube.
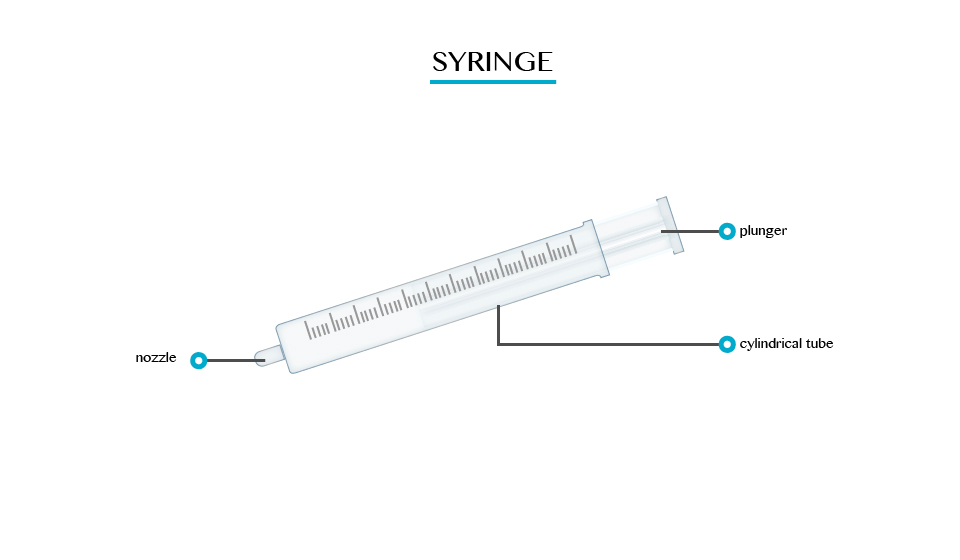
They can be fitted with hypodermic needles and used to administer injections.
They are used to measure liquids and gases in a laboratory.
They are used to apply certain compounds such as a glue or lubricant.
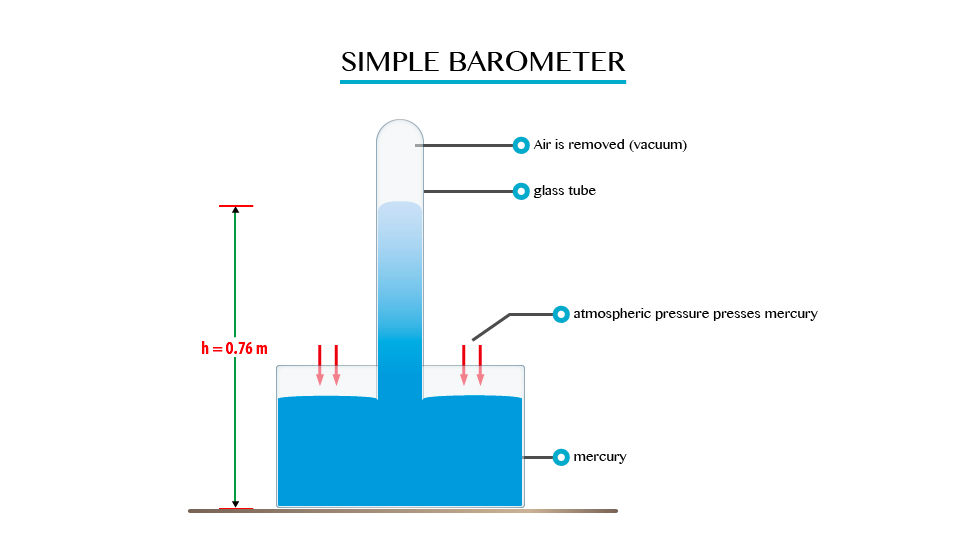
Types of barometer:
- The simple barometer
- Fortin barometer
- Aneroid barometer
A simple barometer consists of a hard glass tube closed at one end.
Fortin barometer
A Fortin barometer is a modified simple barometer. It consists of an inverted tube closed at its upper end with the lower open end immersed in a reserve of mercury. The atmospheric pressure is measured in terms of the height of the column of mercury.
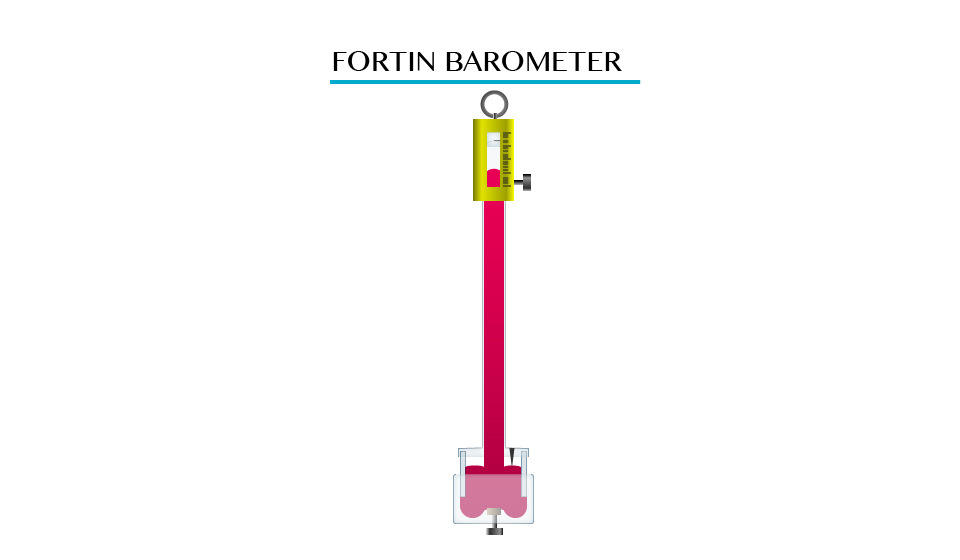
Disadvantages of Fortin barometer:
Mercury is very expensive to use and is very toxic. For these reasons, an aneroid barometer is usually preferred.
It is not portable as it is generally big and contains liquid.
It must be mounted in a vertical position








