TOPIC 1: CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS ~ BIOLOGY FORM 2
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
Kingdom Fungi
General features of kingdom fungi
Fungi are found in damp or wet places
They have eukaryotic cells with a rigid protective wall made of chiti
They are heterotrophs, some are saprophytic where others are parasitic
They store food as glycogen
They reproduce using spore
They are non-mobile
They have chitin in their cell wall
They have septate
The Phyla of the Kingdom Fungi
State the phyla of the Kingdom Fungi
Phyla of the kingdom fungi
- Ascomycota
- Zygomycota
- Basidiomycota
Their cell wall is not made by chitin but cetin polysaccharide component of phosphoric acid
Have granulated cytoplasm
Store food in form of glycogen
Reproduce asexually by budding and sexually by means of ascospores.
- Reproduce sexually by means of ascospores
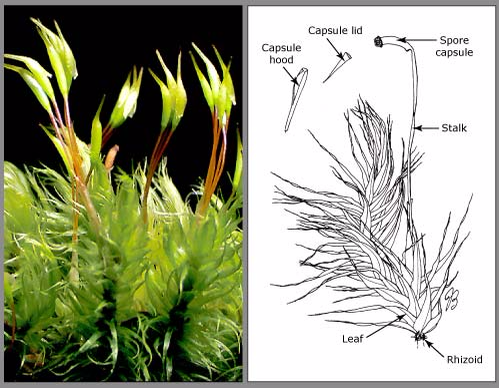
The Structure of Mosses
Describe the structure of mosses
Mosses are small, softplantscalledbryophytes, that are typically 1–10 cm (0.4–4 in) tall, though some species are much larger. They commonly grow close together in clumps or mats in damp or shady locations. They do not haveflowersorseeds, and their simple leaves cover the thin wiry stems. At certain times mosses produce spore capsules which may appear as beak-like capsules borne aloft on thin stalks.
Outline advantage and disadvantages of Mosses
Division Filicinophyta (Pteridophyta)
This division was formerly called Pteridophyta. The division Filicinpphyta includes a group ofprimitive vascular plants. The adult plant body in these plants is a sporophyte. It showsdifferentiation into true roots, stems and leaves. The stem is mostly herbaceous. Leaves may besmaller or larger. Vascular tissues are present in all the vegetative parts of the plant body.
Characteristics of division Filicinophyta
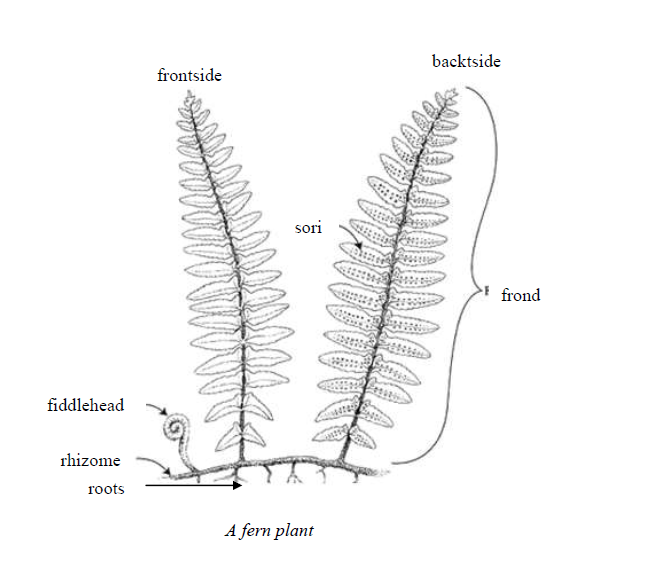
Reproduction involves production of spores inside special structures called sporangia which occur on the underside of the leaves called prophylls. Sporangia may sometimes be found in groups called sori.
The plants may be zoosporous – producing only one type of spore or heterosporous -producing two different types of spores; smaller microspores and larger megaspores.
They are seedless vascular plants, which contain vascular tissues but do not produce seeds.
The Structure of Ferns
Describe the structure of Ferns
Roots are formed from the rhizomes or sometimes from the stipe. The roots usually do not divide once they grow from the rhizome. Tree fern roots grow down from the crown and help thicken and strengthen the trunk. The roots anchor the plant to the ground and absorb water and minerals.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ferns
Advantages of ferns
Some ferns are edible and hence serve as a source of food.
They provide nutrients to the soil to improve soil fertility.
They cover the soil and prevent soil erosion.
They are used as decoration materials.
Disadvantages of ferns
They harbour dangerous organisms like snakes and insects.
Some ferns are poisonous when eaten.