NON METALS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS
connected with their tendency towards electron gain in the course of
formation of compounds:
The oxide of a non-metal is a covalent compound. Being acidic, it
combines with water to form an acid, e.g.
because replacement of hydrogen in an acid is due to the fact that H+ accepts electrons supplied by a metallic atom.


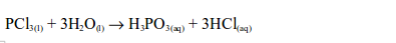
compound is formed by equal sharing of electrons between or among the
combining atoms. For example, methane ammonia, hydrogen chloride and
hydrogen sulphide are the covalent compounds.

electrons from other substances. Therefore, they are called oxidizing
agents because, upon accepting the electrons, the substances donating
these electrons are oxidized. So they act as the agents for oxidation of
other substances.
non-metal accepts one electron while a divalent one accepts two
electrons. The ion formed carries the corresponding number of negative
charges, but they rarely exceed two and never exceed three.
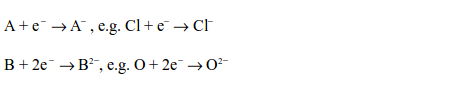
Due to the fact that non-metals accept the electrons(s) donated by
other substances, particularly metals, they are, therefore, termed as oxidizing agents. This is because by accepting the electrons, they help oxidize the electron donors.
the extra electron(s) accepted lead to the formation of negative ions.
The easiness of formation of negative ions depends on the ability of an
element to accept the electrons. The ability of accepting electrons is
called electronegativity of an element. Some elements are more electronegative than others.
power of the element. Elements with higher electronegativity will
displace those elements with lower electronegativity from their
compounds.
to the series above, fluorine will displace all the rest of the
elements from their compounds as it is more electronegative than any
other element in the series. Likewise, chlorine can displace bromine,
iodine and nitrogen from their compounds. The displacement reaction
occurs in the manner:


higher the electronegativity the stronger the oxidant. For example,
bromine is a stronger oxidant than iodine, nitrogen and carbon.
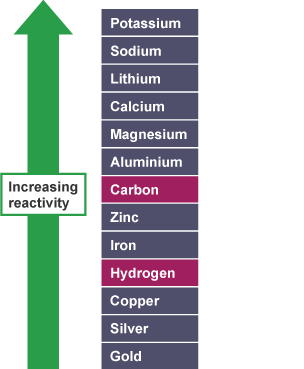
that zinc and iron can bedisplacedfrom theiroxidesusing carbon but not
using hydrogen. However, copper can be extracted using carbon or
hydrogen.
is very reactive, so it is never found as the free element in nature.
It occurs mainly as sodium chloride or rock salt. It also occurs in the
combined state as chlorides of sodium, potassium and magnesium.
industry, chlorine is made by electrolysis of molten sodium chloride or
brine. Brine is a concentrated solution of sodium chloride in water.
the laboratory, chlorine is made by the oxidation of concentrated
hydrochloric acid. The oxidation can be brought about by a number of
oxidizing agents, for example, lead (IV) oxide, manganese (IV) oxide,
trilead tetraoxide (Pb3O4) or potassium manganate (VII).
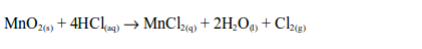
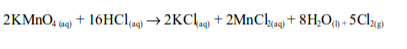
is a useful but dangerous gas. It is very poisonous if inhaled to even a
small extent (1 part of chlorine in 50,000 parts of air causes death).
Chlorine poisoning occurs when the gas is inhaled or swallowed. It
reacts with water inside and outside of the body (such as water in the
digestive tract and moisture on the lungs and eyes) to form hydrochloric
acid and hydrochlorous acid. Both of these substances are extremely
poisonous.
incidents of chlorine poisoning are due to ingesting household cleaners
or bleach products. Due to its poisonous nature, chlorine was used in
the World War I (1914-1918) to kill people and it caused many deaths.
When a little litmus solution is poured onto a gas jar of chlorine,
litmus immediately turns colourless. The gas also bleaches a damp litmus
paper since the gas is acidic. If blue litmus paper is used, it is
first turned red before being bleached. The bleaching action is due to
the fact that chlorine reacts with the water, forming a mixture of
hypochlorous and hydrochloric acids.
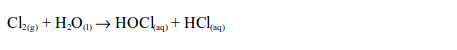
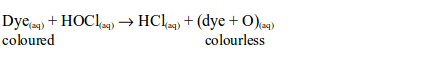
dry chlorine does not bleach. It has to be moist since the hypochlorous
acid formed by its reaction with water is the one that is responsible
for the bleaching action.
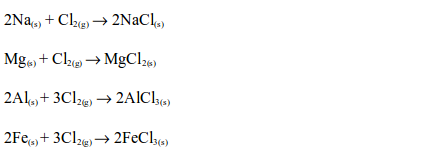

When a filter paper dipped into a little turpentine is dropped into a
gas jar of chlorine, a violent reaction occurs and a black cloud of
solid particles of carbon is formed.
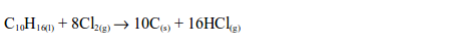
reaction also takes place with other hydrocarbons as well and as with
turpentine, hydrogen chloride gas is formed. The hydrogen chloride can
be shown to be present by passing a little ammonia gas across the top of
the jar whereby dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are observed.

Hydrogen chloride gas is oxidized to elemental sulphur by chlorine gas.
When a gas jar of hydrogen sulphide is inverted over a gas jar of
chlorine, a yellow precipitate of sulphur and hydrogen chloride gas will
be formed.

When a stream of chlorine gas is bubbled through a pale green iron (II)
chloride solution, a red-brown precipitate of iron (III) chloride is
formed, showing that the iron (II) chloride has been oxidized to iron
(III) chloride.
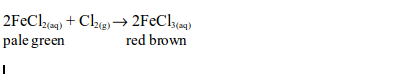
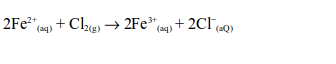
reacts with cold dilute aqueous solution of sodium or potassium
hydroxides, forming a pale yellow solution of the hypochlorite and
chloride of the metal.

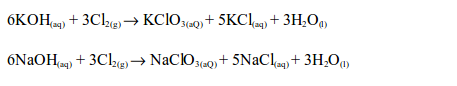
Chlorine is bleaching agent and is also used in the manufacture of
other bleaches. When chlorine is added to sodium hydroxide solution,
bleach is made.
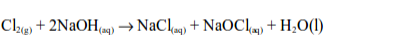
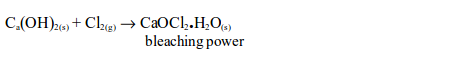
power finds extensive use in dye works, and in laundries. It is used in
industries where cloth, cotton, paper, etc. need to be bleached. Many
textile industries use chlorine for bleaching purposes. Bleach is also
used to kill bacteria for example in the toilet. It will also remove
colour from the dyed materials.
Chlorine is added to water supplied to homes and industries to kill
disease-causing germs like bacteria. If they were not killed, these
pathogens might cause diseases such as cholera and typhoid. It is also
used to sterilize the water in swimming pools.
Chlorine is used to make some important chemicals such as hydrochloric
acid, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), tetrachloromethane (CCl4), and chloroform (CHCl3).
Chlorine is a reactant in the manufacture organo-chloro compounds which
are used to make pesticides, antiseptics (e.g. dettol), herbicides
(weed killers) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) which is an intermediate
compound in the production of plastics.
chloride is a gaseous compound at room temperature. It is usually
prepared in the laboratory by the reaction between concentrated
sulphuric acid and any chloride, e.g. sodium chloride. When a mixture of
the two is gently warmed, hydrogen chloride gas is formed.
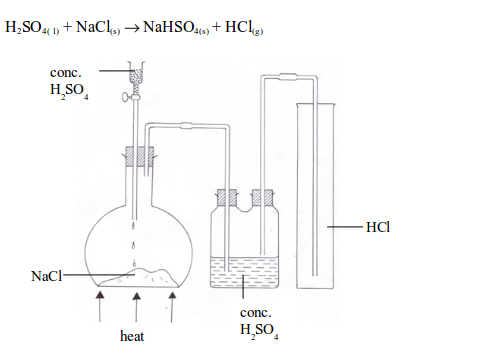
- It is a colourless gas with a choking, irritating smell and an acid taste.
- It is heavier (denser) than air.
- It fumes in most air due to the formation of tiny droplets of hydrochloric acid.
- It is very soluble in water (450 cm3 of gas in 1 cm3 of water). The acidic properties and the solubility of hydrogen chloride gas can best be shown by the fountain experiment
dry sample of hydrogen chloride gas has no effect on dry, blue litmus
paper but it turns moist, blue litmus paper to red. This is due to
acidic properties of hydrogen chlorine gas.

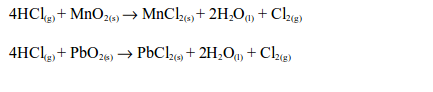
When the gas is passed though a solution of silver nitrate, acidified
with dilute nitric acid, a white precipitate of silver chloride is
formed. This is another test for hydrogen chloride gas and all soluble
chlorides.


chloride gas is very soluble in water (and in other polar solvents). In
water, an acid solution is formed, which is hydrochloric acid. In
aqueous solution, the hydrogen chloride molecule dissociates into
hydrogen ions (H+) and chloride ions (Cl–):

solution is called hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid reacts with
metals, metal oxides, hydroxides (soluble bases) and metal carbonates..
- it turns damp blue litmus paper red;
- it reacts with various substances just like other acids (see table bellow); and
- it conducts electricity, yielding hydrogen gas at the cathode and chlorine gas at the anode.
| Acid reacting with | General equation |
| oxide (base) | acid + metal oxide ® salt + water |
| alkali (soluble base) | acid+metal hydroxide(akali)®salt+water |
| metal | acid + metal ® salt + hydrogen |
| metal carbonate | acid + metal carbonate®salt+water+CO2 |
- It
is chiefly used in the production of hydrochloric acid. When the gas is
dissolved in water in the appropriate proportions, hydrochloric acid is
formed. - Aqueous hydrogen chloride is used in qualitative and quantitative analysis.
- It
is an important reagent in other industrial chemical transformations,
e.g. hydrochlorination of rubber and production of vinyl and alkyl
chlorides. - In the electronics industry, it is used to both rub semiconductor crystals and to purify silicon.
- It is used in the textile industry, to separate cotton from wool and fluff.
- In the laboratory, anhydrous forms of the gas are particularly useful for generating chloride-based Lewis acids.
- It is used to remove rust from the oxidized metals.
- It
is extensively used in the manufacture of medicines and is a key
substance utilized to turn maize and other agricultural products into
artificial sweeteners.
is a yellow, crystalline, non-metallic solid. Its symbol is S. It has
an atomic number of 16. Sulphur exists in nature as a free element and
in compounds.
a free element, sulphur is found in several countries such as Italy,
Mexico, Japan, Poland, USA and Sicily. In its combined state, sulphur is
found combined with metal ores such as galena (PbS), iron pyrites (FeS2), Copper pyrites (CuFeS2) and zinc blend (ZnS). It is also found in natural gas as hydrogen sulphide (H2S) and in crude oil as organic sulphur compounds.
is extracted from its underground deposits by the Frasch process. The
Frasch process makes use of the low melting point (119oC) of sulphur.
this process, a hole about 30 cm in diameter is bored down through the
clay, sand, and limestone to the sulphur beds. This boring is lined with
an iron pipe and inside the pipe, is sunk a device called sulphur pump.
The pump consists of three concentric pipes (cylindrical pipes with a
common centre) which end in a reservoir of a large diameter (see figure
bellow).
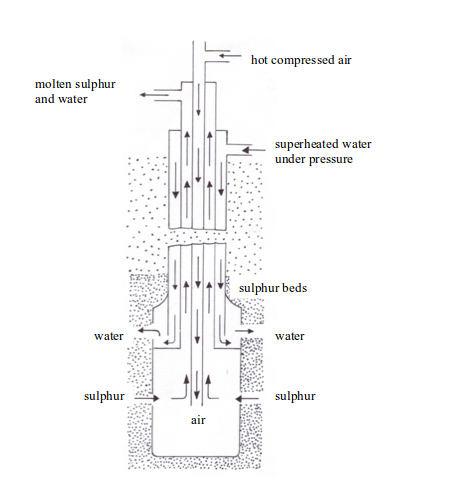
This water must be kept at a pressure of about 10 atmospheres to
maintain it in the liquid state, i.e. it is superheated water, and it is
hot enough to melt the sulphur. The molten sulphur flows into the
reservoir at the base of the pump and is forced up to the surface. The
sulphur obtained is 99.5% pure and can be used without any purification.
- Superheated water (170oC) is pumped through the outer pipe to melt the sulphur.
- Hot
compressed air (10 atm) is pumped down through the inner pipe. The
combination of the hot water and the hot air melts the sulphur. The
molten sulphur, hot air and hot water form a froth. - The froth is forced to the earth’s surface through the middle pipe by the compressed air.
- The molten sulphur is collected in large tanks (where the water drains off), cooled and solidified.
is a relatively reactive element that readily reacts with other
elements to form compounds such as oxides, chlorides and sulphides.
a mixture of iron filings and powdered sulphur, in the proportion of 56
to 32, that is 7:4 (the ratio of their relative atomic masses), is
heated, the two react in a highly exothermic reaction. The heat given
out makes the mixture to continue glowing even after the heating has
stopped. A black or dark grey iron (II) sulphide is formed.



(II) sulphide is not attracted by a magnet since it is not magnetic.
The magnetic property of iron is lost when this compound is formed.

acids do not act upon sulphur. However, sulphur is oxidized by hot
concentrated sulphuric acid with the formation of sulphur dioxide.
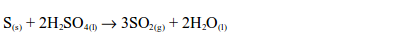

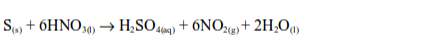
is oxidized by hot concentrates nitric acid to sulphuric acid while
nitric acid is reduced to nitrogen dioxide and water.
- Most
of the sulphur produced in the world (90%) is used to manufacture
sulphuric acid. Sulphuric acid is an important reagent in many
industrial processes. - Sulphur is used in the manufacture of sulphur dioxide (used in the Contact Process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid).
- Manufacture of calcium hydrogensulphite, Ca(HSO3)2, and sodium sulphite which are used for bleaching wood straw and wood pulp in the paper industry.
- It
is also used for vulcanization of natural rubber. Rubber is usually
sticky and soft. When heated with sulphur (vulcanization), it becomes
hard and strong. - It is used for dusting vines to prevent growth of certain kinds of fungi and also as an insecticide.
- Sulphur
is used in smaller quantities for the manufacture of dyes, explosives,
fireworks, gunpowder etc. For example gunpowder is a mixture of
potassium nitrate, carbon and sulphur. - It is used in the
manufacture of various organic compounds such as plastics and
pharmaceuticals like sulphur ointments e.g. sulphadimadine, septrin
e.tc. - Photographic chemicals such as carbon disulphide (CS2) and sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3) are made using sulphur as one of the raw materials.
- Some
is added to cement to make sulphur concrete. Unlike ordinary cement,
this is not attacked by the acid. So it is used for walls and floors in
plants where acid is used.
the laboratory, sulphur dioxide is prepared by heating a mixture of
sodium sulphite and dilute hydrochloric acid. The reaction equation is:
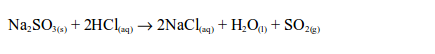
sulphur dioxide can be prepared by heating a mixture of concentrated
sulphuric acid and copper. In this case, there is no reaction until the
mixture in the flask becomes hot. Then rapid effervescence occurs and
the gas is usually collected as shown.
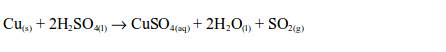
- The gas is colourless with an irritating (pungent), chocking smell.
- It is denser than air. Its density is 2½ times that of air.
- It is readily soluble in water and forms an acidic solution of sulphurous acid.
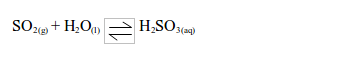
dioxide bleaches the colours in dyes such as flower pigments. When the
flower pigments or dyes contain oxygen, they are coloured. Sulphur
dioxide reduces the dye (removes oxygen from it) and the dye, therefore,
turns colourless. This process can be summarized as follows:
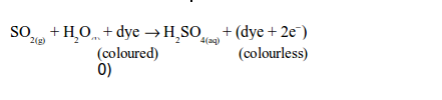

the acid takes up oxygen from the dye of the flowers or paper and forms
sulphuric acid. The removal of oxygen from the dye converts it to a
colourless compound:
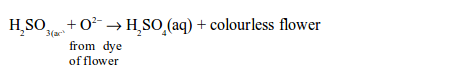
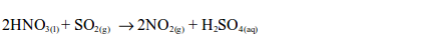
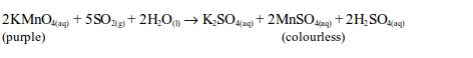
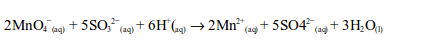
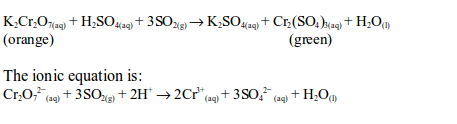
oxidation state of chromium changes from +6 in potassium dichromate
(VI) to +3 in chromic sulphate. On the other hand, sulphur dioxide is
oxidized by the dichromate (VI) to sulphate (SO42–).
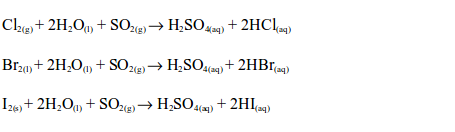
sulphide gas has a smell similar to that of a rotten egg. The hydrogen
sulphide gas is oxidized by sulphur dioxide in the gas jar to sulphur:
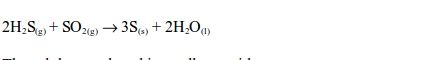
sulphur produced is a yellow residue.The reaction takes place in the
presence of moisture which acts as a catalyst. That is why water is
added in the jar.
burning magnesium is lowered into a jar containing sulphur dioxide gas,
a white solid, magnesium oxide, and yellow pieces of sulphur are
formed:

- The gas can be identified by its characteristic pungent and choking smell.
- It
can also be detected by putting into it a filter paper that has been
previously dipped into an acidified solution of potassium dichromate
(VI). The colour of the filter paper changes from orange to green due to the reduction of dichromate (VI) to chromate (III). - Sulphur dioxide also decolourized acidified potassium permanganate solution.
dioxide has got a number of uses in daily life. However, there are also
some hazards which can be caused by the gas if its production is not
controlled.
- The gas is used in the industrial manufacture of sulphuric acid in the Contact Process.
- It is used as a bleaching agent for wood pulp, silk, wool and straw.
- Its
poisonous nature makes it a useful fumigant. So it is used in
fumigation. The gas is poisonous to all organisms, particularly
bacteria. - It is used as a preservative and sterilizing agent in
making soft drinks and jam, and in dried fruits. A very low
concentration of the gas in food prevents fermentation as it stops the
growth of bacteria and moulds. Its reaction with oxygen prevents
oxidation of juices and other liquids to which it is added for
preservation.
hazards of sulphur dioxide gas are due to its effect in environmental
pollution and the health problems accompanied with that pollution.
Sulphur dioxide is a major air pollutant. The major sources of sulphur
dioxide in the air are power plants that use fossil fuels such as coal,
diesel and petrol; industrial boilers; and exhaust emissions from motor
vehicles. The gas is also produced during metal smelting and other
industrial processes.
of sulphur dioxide output comes from burning coal in coal-fired power
stations. All coal contains small amounts of sulphur. So when the coal
is burnt to produce energy, the sulphur in the coal reacts with oxygen
in the air to produce sulphur dioxide

dioxide is a very irritating gas and is thought to be the cause of
bronchitis and other lung diseases. Exposure to higher concentrations of
the gas can cause impairment of the respiratory function and heart
diseases.
dioxide also causes acid rain. This occurs when the gas comes in
contact with moist air. The sulphur dioxide dissolves in water vapour
from the clouds and combines with oxygen from the atmosphere to form an
acid – sulphuric acid:
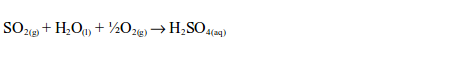
rain damages the leaves and barks of plants making them more vulnerable
to diseases, weather and insects. When acid rain reaches the lake,
river or other water bodies it makes the whole water body acidic. Even a
low concentration of acid in the water can kill fish and other marine
organisms.
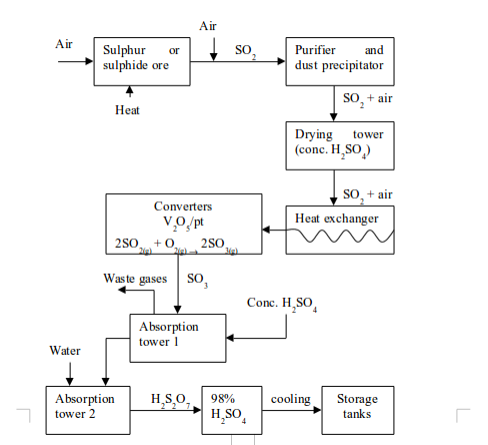
acid is an important laboratory and industrial reagent. It is produced
in large scale through the Contact Process. The process involves four
major stages. These are:
- production of sulphur dioxide;
- purification of sulphur dioxide;
- catalytic conversion of sulphur dioxide (SO2) to sulphur trioxide (SO3); and
- conversion of sulphur trioxide to sulphuric acid.


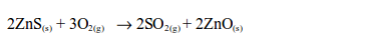
sulphur dioxide produced in the first stage is mixed with air, ready
for passing it over the catalyst. Before contact with the catalyst is
allowed, the gas mixture has to be purified to remove impurities. This
is achieved by passing the mixture through an electrostatic precipitator
to remove any dust. It is then washed with water to remove impurities
such as traces of arsenic (III) oxide (As2O3). The gas mixture is then passed through concentrated sulphuric acid to remove all moisture. The three impurities (As2O3, dust and moisture), if not removed, will poison the catalyst thereby rendering it useless.
purified and dried mixture of sulphur dioxide and air is passed through
a heat exchanger to acquire the necessary heat for the conversion to
sulphur trioxide. The mixture is then taken to the conversion chamber,
which contains a catalyst. The catalyst used is finely divided vanadium
(V) oxide (vanadium pentoxide, V2O5) which is heated to 450°C.
platinized asbestos was used as a catalyst. But, compared to vanadium
(V) oxide, platinum is very expensive and easily poisoned by impurities.
So it has been replaced by vanadium (V) oxide as the usual catalyst
used in the Contact Process.
dioxide remains in contact with the catalyst during the conversion
process, hence the name Contact Process. The reaction that takes place
during the conversion is:
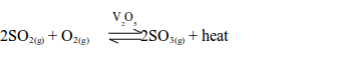
reaction is exothermic, which means that, as sulphur trioxide is
formed, heat energy is released. If the temperature rises above 450°C the yield of sulphur trioxide decreases.
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, a lower temperature should be
used to shift the equilibrium to the right, hence increasing the
percentage yield. However, too low temperature will lower the formation
rate to an economical level. Hence, to increase the rate, high
temperature (450°C), medium pressure (1-2 atm) and a catalyst (V2O5)
are used to ensure maximum yield. The catalyst only serves to increase
the rate of reaction as it does not change the position of the dynamic
equilibrium.
sulphur trioxide from the conversion chamber is passed through a heat
exchanger to remove excess heat. It is then taken to an absorption tower
where it is dissolved in concentrated sulphuric acid to form oleum or fuming sulphuric acid:


dioxide cannot be dissolved directly in water to form sulphuric acid.
The reaction is so highly exothermic that the heat produced vapourizes
the sulphuric acid formed. This makes it difficult to collect the gas
because the acid vapour (mist) produced is very stable and cannot be
condensed.
sulphuric acid reacts with metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides and
metal carbonates and hydrogencarbonates to produce salts.
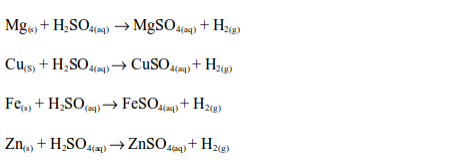
of metal oxides with dilute sulphuric acid are neutralization
reactions. Metal oxides react with dilute sulphuric acid to form a salt
(sulphate) and water, e.g.
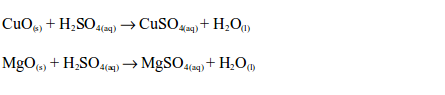
reaction between dilute sulphuric and a metal hydroxide is a
neutralization reaction. Metal hydroxides react with dilute sulphuric
acid to form a sulphate and water, e.g

sulphuric acid reacts with metal carbonates and hydrogencarbonates to
give metal sulphates, carbon dioxide and water, e.g.

a dehydrating agent, it will remove the elements of water (hydrogen and
oxygen) from a compound to form a new compound. It will dehydrate
sugar, paper and wood. These are all made of carbon, hydrogen and
oxygen. The acid removes the hydrogen and oxygen as water, leaving
carbon behind.
concentrated sulphuric acid is added to sugar, a vigorous reaction
occurs, causing the reaction mixture to rise and fill the beaker.
colour of the sugar changes to brown and finally black. Concentrated
sulphuric acid dehydrates sugar (glucose) by taking away the elements of
water (hydrogen and oxygen) from the sugar, leaving carbon.


final product is a black mass of carbon. The reaction is highly
exothermic. The heat produced evaporates the water formed from the
reaction.
acid also dehydrates some hydrated salts. When concentrated sulphuric
acid is added to hydrated blue copper (II) sulphate crystals, the colour
changes from blue to white. The acid dehydrates the hydrated copper
(II) sulphate crystals to anhydrous copper (II) sulphate powder:

a drying agent, concentrated sulphuric acid absorbs traces of water
from substances. Because of its ability to absorb water, it is used for
drying most gases prepared in the laboratory that it would not react
with. It cannot be used for drying ammonia, carbon dioxide, hydrogen
sulphide or any gas with which it reacts.
concentrated sulphuric acid is a strong oxidizing agent. It oxidizes
both metals and non-metals while it is reduced to sulphur dioxide.
sulphuric acid oxidizes charcoal (carbon) to carbon dioxide, sulphur to
sulphur dioxide and copper to copper (II) sulphate.
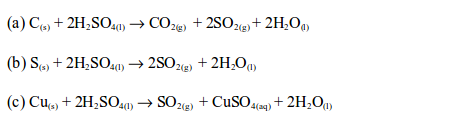
carbon, a white precipitate is formed on the glass rod when the rod
dipped in lime water (calcium hydroxide) is placed in the mouth of the
test tube. This confirms the presence of carbon dioxide gas which reacts
with the calcium hydroxide on the glass rod to produce a white
precipitate of calcium carbonate.

acid is one of the most important industrial chemicals. It has widely
varied uses and plays some part in the production of nearly all
manufactured goods. The following are some of the uses of sulphuric
acid:
- Manufacture of fertilizers
The major use of sulphuric acid is the production of fertilizers such
as ammonium sulphate and superphosphates (phosphate fertilizers). - Manufacture of chemicals
It is widely used in the manufacture of chemicals e.g. in making
hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, sulphate salts,
synthetic detergents, soap, paints and pigments, explosives, plastics
and drugs. - Refining of crude oil A large quantity of sulphuric acid is used in refining crude oil.
- Extraction and manufacturing of metals
Sulphuric acid is used in the iron and steel-making industry to remove
rust and scale from the surface of the rolled iron sheets. It is also
used in processing metals e.g. in pickling (cleaning) iron and steel
before plating them with tin or zinc to produce galvanized iron. - Manufacture of alum
Sulphuric acid is used in the manufacture of aluminium sulphate, which
is used in water treatment plants to filter impurities and to improve
the taste of water. Aluminium sulphate is made by reacting bauxite with
sulphuric acid. - Manufacture of natural and man-made fibres
Sulphuric acid is used for making natural and synthetic (artificial)
fibres. For example, the textile called rayon is made from cellulose
fibres derived from wood. These fibres are dissolved in a solution of
tetraamminecopper (II) sulphate to produce a thick liquid which is then
injected into sulphuric acid to form rayon fibres. - Other uses:Sulphuric
acid is used as (i) an electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, which are
used in cars, to allow the flow of electrons between the plates in the
battery. The sulphuric acid used in this way is called battery acid;
(ii) as a general dehydrating agent in its concentrated form in tanning
leather; and (iii) in waste water treatment.
makes about 78% of the air by volume. The element also occurs combined
with other compounds in the form of sodium nitrate, Chile saltpetre,
NaNO3 (as a mineral deposit in Chile), and in the soil as ammonium sulphate, sodium nitrate, potassium nitrate and calcium nitrate.
nitrogen also occurs as a constituent of all living matter of plants
and animals in the form of proteins, enzymes, alkaloids.


nitrogen evolved may be collected over water because the gas is only
slightly soluble in water, at ordinary temperature, and slightly denser
than air.
the four gas jars of nitrogen gas collected in the previous experiment
(Experiment 1.16), carry out the following tests for nitrogen gas and
write down your observations:
- Remove the cover from the first jar and smell the gas. Observe the colour of the gas and identify its smell.
- Remove the cover from the second jar and put in it a piece of damp universal indicator.
- Place a lighted splint into the third gas jar.
- To the fourth jar, add some calcium hydroxide solution (lime water) and shake.
- The gas is colourless and odourless. This distinguishes it from gases such as sulphur dioxide, ammonia, hydrogen chloride, etc.
- The colour of the indicator does not change. This shows that nitrogen is a neutral gas.
- The
lighted splint is extinguished and the gas does not burn. It can not,
therefore, be any gas which supports combustion, e.g. oxygen, dinitrogen
oxide, or any combustible gas, e.g. hydrogen sulphide, carbon monoxide,
hydrogen, etc. - After the above tests, the only gas with which
nitrogen may be confused is carbon dioxide. To distinguish it from
carbon dioxide, the gas is dissolved in calcium hydroxide solution.
Nitrogen leaves the calcium hydroxide unchanged while carbon dioxide
turns the solution milky (due to formation of a precipitate of CaCO3).
is colourless and odourless. It is slightly less dense than air and
sparingly insoluble in water. The gas is neutral to litmus.
ordinary conditions, nitrogen gas is inert. However, the gas only takes
part in reactions at very high temperature as follows:

Nitrogen does not burn nor does it support combustion. When heated, the
gas combines with oxygen to form nitrogen monoxide gas:


- Manufacture of fertilizers:
Nitrogen is used to manufacture nitrogenous fertilizers. These include
diammonium phosphate (DAP), calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN), ammonium
superphosphate (ASP), ammonium nitrate (AN), ammonium phosphate sulphate
(APS), ammonium sulphate nitrate (ASN), ammonium sulphate (AS) and
urea. - Refrigeration: Because of its
low boiling point (-196oC), liquid nitrogen is used as a refrigerant for
storing organs in research laboratories, bull semen for artificial
insemination, eggs and other cells for medical research and reproductive
technology, etc. It is also used for preservation of food products and
for their transportation. - Processing reactive substances:
Some reactions require an inert atmosphere in order to proceed as
desired. Because of its low reactivity, nitrogen is used to provide an
inert atmosphere for storing and processing reactive substances. - Manufacture of nylon:
Nitrogen is used in the manufacture of synthetic fibres such as
polyamides. Polyamides are commonly known as nylons. Nylons are
chemically inert and are stronger than natural fibres. They are used in
making fishing nets, clothes, ropes, and many other items. - Manufacture of ammonia:
Nitrogen is used in the manufacture of ammonia through the Haber
Process.In the Haber Process, ammonia is manufactured by direct
combination of nitrogen and hydrogen.Nitrogen and hydrogen are mixed in
the ratio of 1:3. The gases are then reacted together at a temperature
of about 450°C and a pressure of 250 atmospheres in the presence of
finely divided iron as a catalyst. N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇔2NH3(g) + heat The
gases are cooled while still under pressure and ammonia is removed as a
liquid. - Manufacture of nitric acid: The ammonia
gas manufactured using nitrogen in the Haber Process is used in the
manufacture of nitric acid by catalytic oxidation. - Plant nutrition:
When atmospheric nitrogen is fixed into the soil by bacterial actions,
it becomes a nutrient to plants. Nitrogen fixation refers to the
conversion of atmospheric nitrogen, by certain species of bacteria, into
nitrites.
is a binary compound of nitrogen and hydrogen. Ammonia gas is
colourless and has a strong pungent and choking smell. It does not occur
free in air, but exists in nitrogenous organic materials such as hoofs
and horns of animals. The gas can be released by heating or burning
these materials.
is prepared in the laboratory by heating any ammonium salt with an
alkali. In most cases, ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide (the
cheaper alkali) are used. Both are solid so they must be thoroughly
ground first to give a very fine mixture so that the reaction can occur
efficiently.
hydroxide reacts with ammonium chloride to produce ammonia gas, calcium
chloride and water. The flask is tilted to prevent any condensed water
formed from running back into the hot flask, which might break it.
gas is dried by passing it over quicklime because it reacts with all
the usual drying agents. Concentrated sulphuric acid is acidic and would
absorb the gas forming a salt e.g. 2NH3(g) + H2SO4(l) → (NH4)2SO4(s)
is less dense than air and very soluble in water, so it is collected as
shown by upward delivery (or downward displacement of air).
- It is a colourless poisonous gas with a strong chocking smell.
- It is less dense than air.
- It is easily liquefied by cooling to -33°C or by compressing it.
- It turns wet, red litmus paper blue as it is the only common alkaline gas
- It
is very soluble in water forming alkaline solution. Ammonia has the
highest solubility of all known gases. About 800 volumes of the gas
dissolve in 1 volume of water at 15°C. The fountain experiment below
demonstrates this solubility.
- Burning ammonia in an oxygen-rich atmosphere; and
- Use of a catalyst.
source of ammonia gas in this experiment is concentrated ammonia
solution which gives off fumes of ammonia gas. If some concentrated
ammonia solution is left in a stoppered flask for a few minutes, the
flask will quickly become full of ammonia gas by diffusion.
catalyst used is the metal platinum. The platinum coil is heated in a
bunsen flame until it is red hot. It is then lowered into a flask
containing ammonia. The coil continues to glow even though it is not
being heated. This indicates that a chemical reaction is taking place.
Near the top of the flask brown fumes can be seen.
as the nitrogen monoxide gas moves towards the neck of the flask and
comes into contact with the air, it reacts with the oxygen in the air to
form nitrogen dioxide gas which is brown in colour. Hence, the brown
fumes are seen at the neck of the flask.
ammonia gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide, the gas is
oxidized to nitrogen and water by the hot copper (II) oxide while the
oxide is reduced to copper.
test is simply performed by dipping a glass rod into concentrated
hydrochloric acid then holding the glass rod at the mouth of a gas jar
containing ammonia gas.
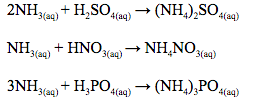
nitrogenous fertilizers manufactured using ammonia include ammonium
sulphate nitrate (ASN), diammonium phosphate (DAP) and calcium ammonium
nitrate (CAN)
- Ammonia comes as a gas or a concentrated solution which is less easy to store; it is easier to store the solid ammonium salts.
- Ammonia is alkaline and can affect the natural pH of the soil.
- Ammonia easily evaporates if directly applied to the soil.
lot of the ammonia from the Haber Process is used to make nitric acid.
The raw materials for manufacture of nitric acid are ammonia, air and
water.

solution is very useful in cleaning. This is because it softens water
in homes and laundries and neutralizes acid stains caused by
perspiration, hence making washing easier. It is also used as a grease
solvent.
ammonia is used in large-scale refrigerating plants such as in ships
and warehouses. It used to be used in domestic refrigerators, but has
now been replaced by non-toxic, non-corrosive chlorofluorohydrocarbons
(CFHs).
carbon forms less than one percent of the earth’s crust by weight, it
is the most interesting of all elements. This is because of the
following reasons:
- All living things are made of carbon and its compounds.
- Over ¾ of the world’s power is obtained from carbon and its compounds.
- Over ¾ of all substances in the world are made of carbon.
is not commonly found in a free state. The free element is mainly found
as graphite and diamond. Carbon occurs in a number of other forms, e.g.
wood charcoal, animal charcoal, coke, soot (lampblack).
compounds are found in many naturally occurring substances such as
coal, petroleum, wood, coal gas, natural gas, carbonates, shells,
organic matter of all kinds, all living things, and occurs in the air to
a small, but very important extent (0.03 – 0.04% by volume) as carbon
dioxide. The carbohydrates, proteins and lipids in all living things
contain carbon.
carbon is found in the form of diamond in Tanzania (Mwadui), Sierra
Leone, India, South Africa, Russia and South America; and impure carbon,
as graphite, is found in Sri Lanka.
element that exists in more than one form is said to exhibit allotropy.
Allotropy is the existence of an element in more than one form (without
change of state). The various forms are known as allotropes.
of a given element differ in their physical properties and may differ
in some chemical properties as well. The allotropic forms of carbon are:
- graphite;
- diamond; and
- amorphous carbon.
allotropes have got different molecular structures. The structural
differences are mainly due to the way their atoms are packed.
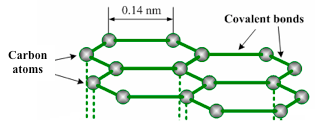
has a layer structure. Figure 1.18 illustrates one layer of the
structure of graphite. Each layer consists of carbon atoms covalently
bonded together into hexagonal rings. These rings form flat parallel
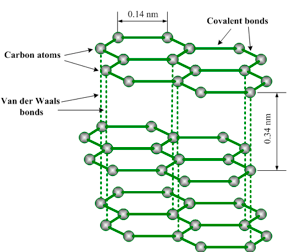
layers, one over the other. The force that hold the carbon atoms
together are very strong. Adjacent layers are held together by weak van
der Waals’ forces as shown in figure 1.19. The layers readily slide over
one another, accounting for the soft and greasy texture of graphite.
atom has got four electrons in its outer shell. Each carbon atom forms
three covalent bonds to other carbon atoms. Thus, three of its four
outermost electrons are paired up to form covalent bonds. The fourth
electron is not attached to any particular atom (delocalized) and is
free to move anywhere along the layers. Graphite conducts electricity in
the plane of the layers but not at right angles to them.
conduction of electricity involves movement of unshared electrons from
one atom to another atom, graphite is a good conductor of electricity
since the hexagonal layers permit this movement. It is also a good
conductor of heat for a similar reason.
- It is a black, soft and slippery substance. It feels soapy and greasy. It has a metallic lustre and is opaque to light.
- It has low relative density (2.3) as compared to diamond (3.5)
- Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity due to the delocalized electrons.
- It
has a very high melting point (3730°C) and boiling point (4830°C). The
melting and boiling points are high because of strong covalent bonds
between the carbon atoms which require more energy (heat) to break in
order to melt graphite.
- It
is used as an electrode in electrolysis and as a positive terminal in
dry cells. The use of graphite as electrode in electrolysis has an
advantage because it does not react readily with most substances (it is
an inert electrode). - It is used as a lubricant, particularly
when high temperatures are involved, where the usual lubricating oils
easily decompose due to extreme heat. It is a lubricant for dynamos,
electric motors and fast-moving parts of machinery. - The major
use of graphite is in making lead pencils of different hardness, by
mixing it with different proportions of clay. The weakly held layers of
carbon atoms in graphite easily slide over each other and are left
behind on paper as black marks. - Being resistant to chemicals and
having a high melting point and also because it is a good conductor of
heat, graphite is used to make crucibles. - Graphite has the
ability to absorb fast-moving neutrons, thus, it is used in nuclear
reactors to control the speed of the nuclear fission reaction.
basic unit of the diamond structure is shown in figure 1.20. Each
carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms. This basic
unit is repeated in three dimensions as shown in figure 1.21 to form a
giant tetrahedral structure of millions of carbon atoms, all forming
four covalent bonds to each other. The melting point of diamond is high.
This is because of the strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms,
which require a large amount of heat energy to break up.
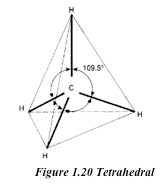
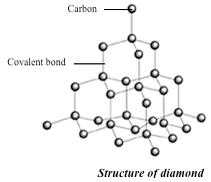
- It
is the hardest natural substance known. This due to the strong covalent
bonds between the carbon atoms in diamond. Again the compact
tetrahedral arrangement of carbon atoms contributes to its hardness. - It has the highest melting point (3550°C) and boiling point (4289°C).
- It has a high relative density (3.5) compared to graphite (2.3)
- It
is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. This is because there are
no free electrons to conduct electricity. All electrons are firmly held
in covalent bonds. - It is colourless, transparent and has a dazzling (amazing) brilliant lustre and radiance.
- It
has a high refractive index of 2.5. The high refractive index results
in high dispersion of light, making it suitable for use in jewellery.
- It is used in making jewellery.
- Due
to its extreme hardness, it is used to make glass cutters, drilling
devices, rock borers, and as an abrasive for smoothing very hard
materials.
| Diamond | Graphite |
| 1. Colourless, transparent andglittering | Black, opaque with metallic lustre |
| 2. Hardest natural substanceknown, used to cut glass andin drills | Soft to touch, greasy or soapy, can be used as a lubricant and in making lead pencils |
| 3. High relative density (3.5) | Low relative density (2.3) |
| 4. Non-conductor | Good conductor of heat and electricity |
| 5. Burns in air least readily (atabout 900°C) | Burns in air readily (at 700°C) |
| 6. Have strong C-C covalentbonds arranged octahedrally toform a giant molecular crystal | Have strong C-C bonds within the hexagonal rings in the sheets but weak Van der Waal’s forces in between layers. |
| 7. Its cleavage is difficult and itoccurs along the boundaries ofthe octahedral crystal unit | Cleavage easy, and occurs along the sheets or the layers. |
| 8. Prepared from graphite at very high pressure and temperature | Prepared from coke and silica mixture at high temperature |
| 9. Not attacked by potassiumchlorate and nitric acid together | Attacked by these reagents |
proof that diamond and graphite are both allotropic forms of carbon can
be shown experimentally by burning equal masses of each allotrope in a
stream of oxygen. It is found that equal masses of each allotrope
produce equal masses of carbon dioxide. C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
weight of carbon dioxide produced can be determined by allowing it to
be absorbed in a weighed amount of potassium hydroxide solution. 2KOH(aq) + CO2(g) → K2CO3(aq) + H2O(l). Then, the weight of carbon dioxide is obtained by calculations based on the equation above.
carbon is carbon that does not have any clear shape, form or
crystalline structure. Amorphous carbon is made of tiny bits of graphite
with varying amounts of other elements considered as impurities. It is
formed when a materials containing carbon is burned in a limited supply
of oxygen, resulting in incomplete combustion.
- Charcoal
- Lampblack (soot) or carbon black
- Coke
is made by heating organic material (animal or plant parts) to a high
temperature in the absence of air or in the presence of limited amounts
of oxygen or other reagents, catalysts, or solvents. This process is
called destructive distillation. There are three categories of charcoal,
namely, wood charcoal, animal charcoal and sugar charcoal.
charcoal is made by heating wood or other vegetable matter (for example
coconut shells) in the almost complete absence of air. Wood charcoal is
light, porous and is a remarkably good absorbent for liquid or gases (1
cm3 of wood charcoal will absorb 100 cm3 of ammonia gas at 0°C).
- Because
of its ability to absorb large amounts of gas or liquid, it is used in
gas masks to absorb poisonous gases in air in industrial process to
recover volatile materials from waste gases. - Wood charcoal can be used in metal refining instead of coke.
- Wood charcoal is a good source of energy. Thus, it is used as fuel for cooking and heating in homes.
charcoal is made by heating animal bones in the absence of air. Its
main component is calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2, and carbon constitutes
about 10% of the components.
charcoal is a very pure form of carbon, and is made by removing the
elements of water (oxygen and hydrogen) from sugar. This is achieved by
using strong dehydrating agents such as concentrated sulphuric acid or
concentrated nitric acid, which removes water from sugar.
is produced by burning petroleum or any hydrocarbon in a limited supply
of air (or in chlorine). It can also be produced from the burning of
organic material at home. It is commonly found in the kitchen chimneys,
lamps and on bases of cooking pans and pots.
- It is used in making printers’ ink, shoe polish and carbon papers.
- It is an important industrial material in the manufacture of tyres. It is used as a filler material in tyres.
is made by destructive distillation of coal. During the process, coal
is obtained as the major product. The other products formed when coal is
destructively distilled are coal gas, coal tar, coal oil, gas carbon
and ammonia liquor.
- Coke is used as a fuel and as a reducing agent in the extraction of iron, lead and zinc. It is also used as a fuel in boilers.
- It is used in the manufacture of producer gas and water gas.
- Carbon burns in excess oxygen to form carbon dioxide C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g).In insufficient oxygen, carbon monoxide is formed.2C(s) + O2(g) → 2CO(g)
- Carbon
has got reducing properties and thus acts as a reducing agent. Carbon
reduces oxides of metals below it in the electrochemical and activity
series to their respective metals. This occurs on strong heating, and
this reaction is used industrially for extraction of metals from their
ores:PbO(s) + C(s) → Pb(s) + CO(g);Fe2O3(s) + 3C(s) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO(g);ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g). - Sulphur vapours react with red hot carbon to give carbon disulphide. C(s) + 2S(g) → CS2(l)
- Carbon dioxide is reduced by red hot carbon to carbon monoxide C(s) + CO2(g) → 2CO(g);This reaction is used in the industrial manufacture of producer gas.
Carbon Dioxide
dioxide is one of the oxides of carbon. The gas is present in the air
at a level of approximately 0.03% by volume. It is also found dissolved
in water. The gas is one of the by-products of all decaying organic
matter. Without carbon dioxide there is no life on earth. It is used by
all plants in the process of photosynthesis and both plants and animals
evolve carbon dioxide in respiration.
dilute hydrochloric acid is poured on marble chips, effervescence
occurs. Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with the marble chips to give
calcium chloride, water and carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide is a colourless and odourless gas.
- It is denser than air.
- When
the gas is cooled to –78°C, it turns straight into the solid (it
sublimes). Sublimation is the change of a gas straight into a solid or
change of a solid straight into a gas. Solid carbon dioxide is called
dry ice. It sublimes when it is heated or exposed to air. - It has a melting point of –199°C and boiling point of –91.5°C.
- Carbon dioxide does not support combustion. This is why it is used in fire extinguishers.
a little carbon dioxide gas is bubbled into lime water (calcium
hydroxide solution), the solution turns milky. This is due to the
formation of a white precipitate of insoluble calcium carbonate.
is a confirmatory test for the presence of carbon dioxide. The test
serves to distinguish carbon dioxide from any other gas.
excess carbon dioxide is bubbled into the lime water, the white
perceptible dissolves to form a clear solution of soluble calcium
hydrogen carbonate: CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) → Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
a burning magnesium ribbon is lowered into a gas jar containing carbon
dioxide gas, it continues to burn for a short time with a spluttering
flame. A white ash of magnesium oxide and black specks of carbon are
formed. The black specks of carbon can be seen on the sides of the gas
jar.
dioxide reacts with water to form a weak carbonic acid. When carbon
dioxide is bubbled into water, it dissolves to form a weakly acidic
solution of carbonic acid:
solution turns a blue litmus paper pink. This indicates that the
solution is slightly acidic and hence too weak to turn the blue litmus
paper to red (as strong acids do). The solution has no effect on red
litmus paper.
Uses of Carbon Dioxide include:
Fire extinguisher:
Carbon dioxide is inert (i.e. it does not burn). It is dense than air
and does not support combustion. Hence, it is a very useful
fire-fighting chemical. When applied to fire, it forms a blanket over
the burning material. Thus, it prevents air (oxygen) from reaching the
burning material and therefore, extinguishing the flames.
Manufacture of aerated (fizzy) drinks:
Soda water and mineral water contain carbon dioxide dissolved under
pressure. Because the gas is only slightly soluble, it is bubbled into
these drinks under pressure to make more of it dissolve. When the
bottles are opened, the gas escapes and it causes the “fizzy”.Dissolved
carbon dioxide is responsible for the pleasant taste of soft drinks such
as lemonade, Coca cola, Pepsi cola and other aerated drinks and mineral
waters. Other beverages like beers are also bottled together with
carbon dioxide.
Refrigeration: Carbon dioxide
is used for refrigeration purposes (i.e. in the deep-freezing of foods).
The gas liquefies at ordinary pressure to form dry ice which sublimes
at -78°C. Dry ice is a good refrigerant because it leaves no liquid
after sublimation as is the case with ordinary ice.
Manufacture of sodium carbonate by the Solvary Process:Carbon
dioxide is used in the manufacture of anhydrous sodium carbonate in the
Solvary Process. The sodium carbonate produced is used in the
manufacture of glass.
Manufacture of baking soda:
Carbon dioxide is used in making baking soda (sodium bicarbonate).
Baking soda is prepared by passing carbon dioxide into cold concentrated
sodium hydroxide solution: CO2(g) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2CO3(aq) + H2O(l).Further
addition of carbon dioxide produces sodium bicarbonate which, at
sufficiently high concentration, will precipitate out of the solution as
a solid: Na2CO3(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) → 2NaHCO3(s)
Yeast and sodium bicarbonate (hydrogencarbonate) are important in the
baking industry. Thus in baking of bread, yeast is added to flour, sugar
and water (forming the dough). In the making of cakes, baking powder (a
mixture of bicarbonate and an acid) is used instead of yeast.
Rain making:
When pieces of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) are dropped into clouds,
the temperature of the clouds is lowered to such an extent that rain
precipitates out.
Photosynthesis: Plants use carbon dioxide from the air to manufacture their own food through the process of photosynthesis








