LABORATORY PRACTICE
A Laboratory is a room or a building designed specifically for carrying out experiments.
You should only enter the lab in the presence of a lab attendant.
Keep all exits and entrances to and from the lab clear of obstructions.
Don’t eat or drink in the lab.
Solid objects should not be thrown into the sink or water ways.
Don’t use any lab container for drinking or storing food.
Make sure that you wash your hands with soap before you leave the lab.
The cover or stopper of a particular chemical must be replaced immediately after use.
After experiments, clean your bench and leave it dry and well arranged.
Never quarrel or fight in the lab.
Never use ungloved hands to hold hot objects
All experiments which produce poisonous fumes must be conducted in the fume chamber.
Lab floor should not be polished to avoid slipperiness.
Lab should have large windows and doors should be opened outwards.
Ensure that the fire extinguisher is fixed to an appropriate place ready to be accessed in case of fire.
In a multi storey building, a physics lab should be in the lowest floor.
| Contents | Uses |
| 1. Pair of scissors | To cut adhesive tapes, bandages and gauze |
| 2. Rolls of adhesive tape | To hold firmly into wounds bandages, gauze and cotton wool |
| 3. Bandages and cotton wool | To clean and cover wounds |
| 4. Sterilised new razor blades | Used when treating new or old wound |
| 5. Sterilised wound | To clean and cover wounds |
| 6. Safety pin | To tighten clip bandages |
| 7. One jar of petroleum jelly | To apply on burns |
| 8. Iodine tincture | To clean fresh cuts and bruises |
| 9. Soap | To wash hands and wounds |
| 10. Antibiotic solution. | To clean wounds |
These are substances can explode. An explosion is a forceful rapid reaction which involves the throwing off particles at high speeds.
The sign means that it is dangerous to keep explosives in glass containers.
This is a chemical/substance that helps a burning substance to burn faster.

Oxidising agent makes a small fire to become bigger. Heating a mixture of an organic material with an oxidising agent may cause explosion. Eg; heating potassium permanganate with saw dust.
These substances catch fire easily. They should not be kept near open flames. If heated,anelectric heater should be used.

Corrosive
These substances burn skin as well can corrode floors and desktops.
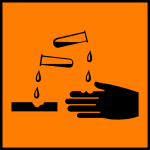
If by accident, a corrosive substance comes into contact with your skin, go to the sink and wash your skin with a lot of water. Examples; Concentrated mineral acids like HCl and HNO3 II. Concentrated alkalis like NaOH and KOH

Harmful – these substances may cause illness or endanger your health. They won’t kill instantly but they are lethal. Irritating substances- cause pain in eyes or on your skin and can endanger your health if you are in contact with them doe too long.

Basic Principles of Science Investigation
Scientific investigation refers to the step-by-step procedures and methods employed in carrying out a scientific research.
Identification of a problem: This is the first step where a problem is recognized. It provides explanations to the day-to-day questions which we come across in our lives Eg; It is observed that despite adequate feeding, vaccination, treatment and spacious rooms, hens lay fewer eggs each day. What is the cause of the fewer number of eggs?
Formulation of hypothesis: Hypothesis is an intelligent guess or a tentative explanation for the observation made. Using the example of a few eggs laid by hens per day the hypothesis could be; a smaller number of eggs are laid because of unusual high temperature in the room. In order to prove this hypothesis, an experiment have to be carried out.
Experimentation: The experiment involves a series of investigations intended to discover relationships or certain facts that may lead to the acceptance, rejection or modification of a hypothesis. The first step in experiment is to construct a plan of investigation.
Observation and data recording: After setting up the experiment, a researcher makes careful observation using their sense organs and records all events that considers relevant.
Interpretation of data: Once a researcher has collected data, he should try to explain the meaning of the experiment. This is an attempt to interpret the data. The data may be presented in a form of a table, bar chart, histogram or even graph.
- Conclusion: This is either confirmation or rejection of hypothesis.
is a set scientific assumptions consistent with one another and supported by evidence but not fully proved (is a hypothesis with more evidence). Fact is a proved theory supported by evidence Hypothesis →Theory →Fact Scientifc Investigation Methods in Solving Problems Use the scientific investigation methods in solving problems Activity 2 Use the scientific investigation methods in solving problems
FORM ONE PHYSICS TOPIC 2: INTRODUCTION TO LABORATORY PRACTICE
Hypothesis →Theory →Fact
Use the scientific investigation methods in solving problems








