Wrong Entries
Identify wrong entries
An accounting error is a non-fraudulent discrepancy in financial documentation. The term is used in financial reporting.
Types of accounting errors include:
- Error of omission — a transaction that is not recorded.
- Error
of commission — a transaction that is calculated incorrectly. One
example of an error of commission is subtracting a figure that should
have been added. - Error of principle — a transaction that is not
in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles ( GAAP).
One example of an accounting error of principle is an expenditure that
is placed in an inappropriate category.
Accounting
errors can occur in double entry bookkeeping for a number of reasons.
Accounting errors are not the same as fraud, errors happen
unintentionally, whereas fraud is a deliberate and intentional attempt
to falsify the bookkeeping entries.
errors can occur in double entry bookkeeping for a number of reasons.
Accounting errors are not the same as fraud, errors happen
unintentionally, whereas fraud is a deliberate and intentional attempt
to falsify the bookkeeping entries.
An
accounting error can cause the trial balance not to balance, which is
easier to spot, or the error can be such that the trial balance will
still balance due to compensating bookkeeping entries, which is more
difficult to identify.
accounting error can cause the trial balance not to balance, which is
easier to spot, or the error can be such that the trial balance will
still balance due to compensating bookkeeping entries, which is more
difficult to identify.
Preparation of a Corrected Trial Balance
Prepare a corrected Trial Balance
An
adjusted trial balance is a listing of all company accounts that will
appear on thefinancial statementsafter year-end adjusting journal
entries have been made.
adjusted trial balance is a listing of all company accounts that will
appear on thefinancial statementsafter year-end adjusting journal
entries have been made.
Preparing
an adjusted trial balance is the fifth step in theaccounting cycleand
is the last step beforefinancial statementscan be produced.
an adjusted trial balance is the fifth step in theaccounting cycleand
is the last step beforefinancial statementscan be produced.
There
are two main ways to prepare an adjusted trial balance. Both ways are
useful depending on the site of the company and chart of accounts being
used.
are two main ways to prepare an adjusted trial balance. Both ways are
useful depending on the site of the company and chart of accounts being
used.
You
could post accounts to the adjusted trial balance using the same method
used in creating the unadjusted trial balance. The account balances are
taken from the T-accounts or ledger accounts and listed on the trial
balance. Essentially, you are just repeating this process again except
now the ledger accounts include the year-end adjusting entries.
could post accounts to the adjusted trial balance using the same method
used in creating the unadjusted trial balance. The account balances are
taken from the T-accounts or ledger accounts and listed on the trial
balance. Essentially, you are just repeating this process again except
now the ledger accounts include the year-end adjusting entries.
You
could also take the unadjusted trial balance and simply add the
adjustments to the accounts that have been changed. In many ways this is
faster for smaller companies because very few accounts will need to be
altered.
could also take the unadjusted trial balance and simply add the
adjustments to the accounts that have been changed. In many ways this is
faster for smaller companies because very few accounts will need to be
altered.
Note
that only active accounts that will appear on the financial statements
must to be listed on the trial balance. If an account has a zero
balance, there is no need to list it on the trial balance.
that only active accounts that will appear on the financial statements
must to be listed on the trial balance. If an account has a zero
balance, there is no need to list it on the trial balance.
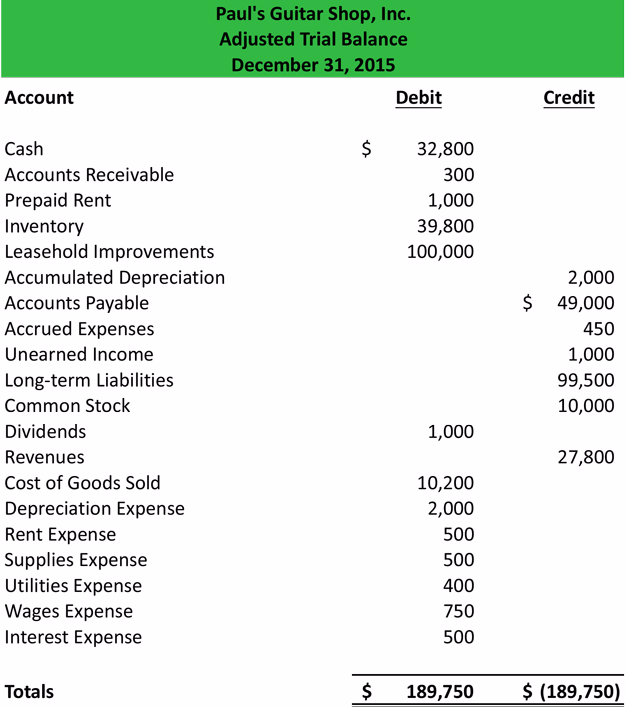
Example 1
Using Paul’sunadjusted trial balanceand hisadjusted journal entries, we can prepare the adjusted trial balance.
Once
all the accounts are posted, you have to check to see whether it is in
balance. Remember that all trial balances’ debit and credits must be
equal.
all the accounts are posted, you have to check to see whether it is in
balance. Remember that all trial balances’ debit and credits must be
equal.
Now that the trial balance is made, it can be posted to theaccounting worksheetand thefinancial statementscan be prepared.
Uses of the Trail Balance
Outline uses of the Trail Balance
Keeping in mind the definition of the trial balance we can define the following characteristics and use of the trial balance:-
- Trial
balance is prepared in tabular form only. It contains debit column for
debit balance of accounts and credit column for credit balances of
accounts. - Only the closing balances of the accounts are shown in trial balance.
- The closing balance of stock is never shown in trial balance. It is always shown as foot note.
- Other
adjustments against which no entries are passed in the books also not
shown in trial balance. They are also shown as footnotes. - The trial balance is prepared on a particular date as required by the management or at the end of thefinancial year.
- Trial balance is not an account. It is a statement only.
- The balance of all accounts is shown at one place. Thus it is the summary of all accounts.
- It shows the arithmetical mistake of the entries.
- Trading,profit and loss accountand thebalance sheetare prepared with the help of trial balance only.

















Leave a Reply