5E Model
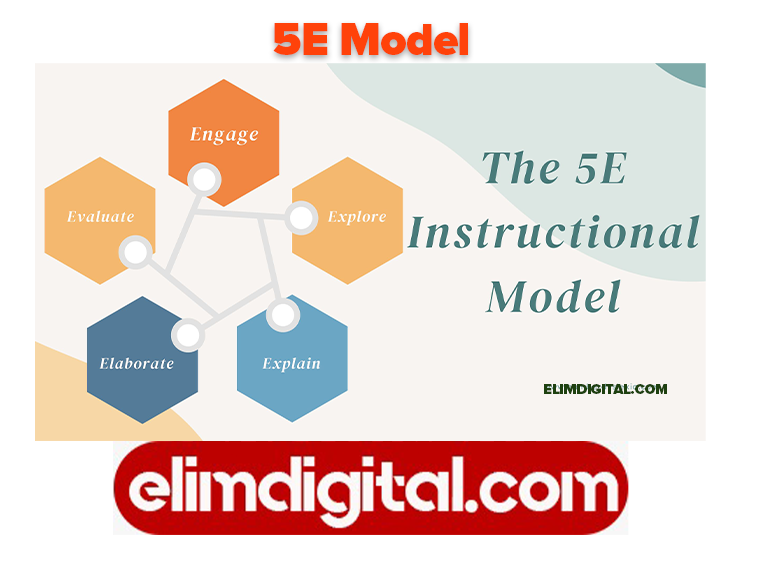
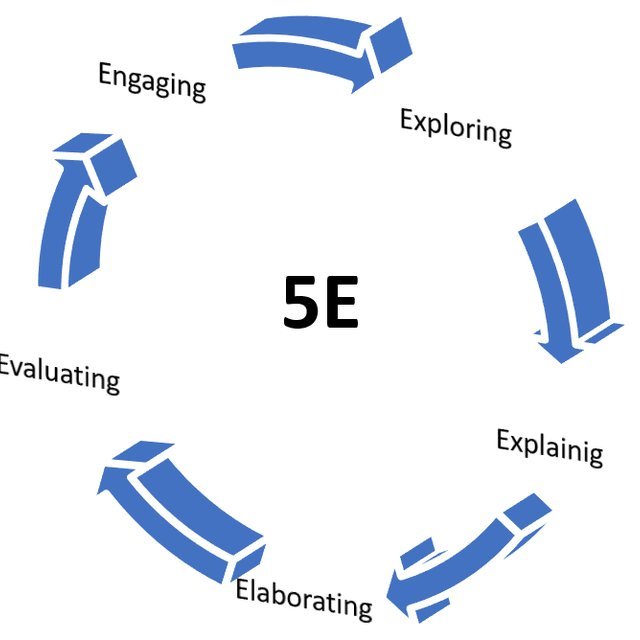
The 5E Model is an instructional framework used in inquiry-based learning to promote active, hands-on, and student-centered learning.
It consists of five phases: Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate. This model is widely used in science education but can be applied across various subjects.
The 5 Phases of the 5E Model:
1. Engage
Does the lesson engage students by bridging gaps in prior knowledge and
sparking curiosity? Are relevant technical, sub-technical, and everyday vocabularies
identified and explicitly taught?
-
Purpose: Capture students’ interest and activate prior knowledge.
-
Activities:
-
Asking thought-provoking questions.
-
Showing a puzzling phenomenon (e.g., a science demo).
-
Discussing real-world connections.
-
-
Example:
-
“Why do ice cubes melt faster on a metal surface than on wood?”
-
2. Explore
Are students encouraged to explore concepts through active participation?
Are open-ended “why” and “how” questions used to stimulate 21st Century skills that
includes communication skills?
-
Purpose: Students investigate concepts through hands-on activities.
-
Activities:
-
Experiments, simulations, or group investigations.
-
Collecting and analyzing data.
-
-
Example:
-
Students test how different materials conduct heat.
-
3. Explain
Does the teacher facilitate understanding by explaining concepts clearly
with language support? Are learners provided with opportunities to ask questions or
encouraged to participate in discussions during class to enhance their listening and
speaking skills as a means to develop conversational abilities?
-
Purpose: Students articulate their understanding, and the teacher clarifies concepts.
-
Activities:
-
Teacher introduces formal terms and explanations.
-
Students present findings and discuss conclusions.
-
-
Example:
-
Teacher explains thermal conductivity after students observe heat transfer.
-
4. Elaborate
Are students given opportunities to apply what they’ve learned in
meaningful ways? Are students taught effective note-taking methods to summarize
and synthesize information?
-
Purpose: Extend learning to new contexts for deeper understanding.
-
Activities:
-
Applying knowledge to real-world problems.
-
More complex experiments or case studies.
-
-
Example:
-
“How does insulation in houses help save energy?”
-
5. Evaluate
Are students assessed on their grasp of both content and language
objectives?
-
Purpose: Assess student learning through formal and informal methods.
-
Activities:
-
Quizzes, presentations, or reflective discussions.
-
Teacher observes and provides feedback.
-
-
Example:
-
Students design an experiment to test heat retention in different materials.
-
5E Model
Benefits of the 5E Model:
✔ Encourages critical thinking and inquiry.
✔ Makes learning student-centered rather than lecture-based.
✔ Helps students construct knowledge through exploration.
✔ Supports long-term retention of concepts.
When is it Used?
-
Science lessons (e.g., physics, chemistry, biology).
-
STEM/STEAM education.
-
Project-based learning (PBL).